Understanding Melanoma
*Please note: This slide show represents a visual interpretation and is not intended to provide, nor substitute as, medical and/or clinical advice.
What is melanoma?
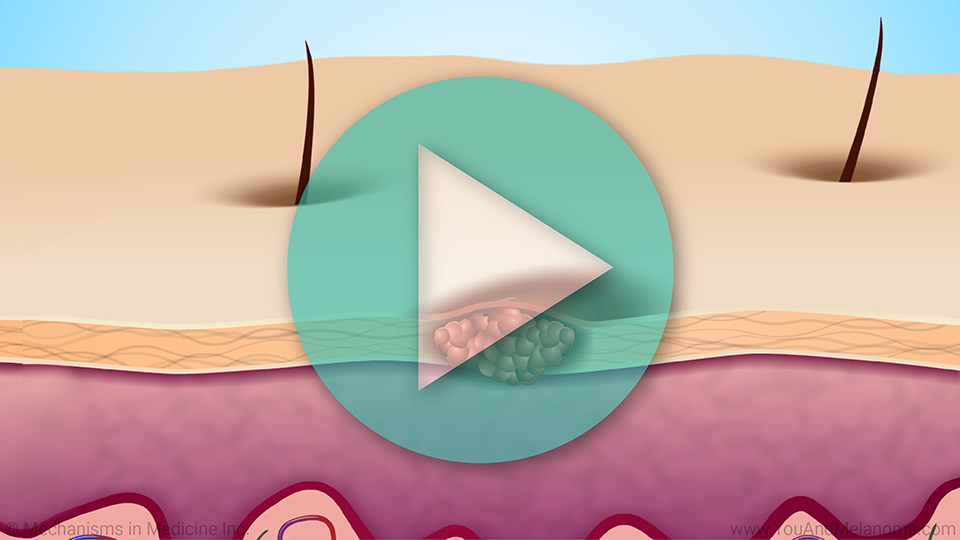
Melanoma is a type of cancer that begins most often in the skin. Less frequently, melanoma can occur in the eye or in mucous membranes such as the nasal passages, mouth, throat, vagina, or rectum.
Melanoma develops in cells called melanocytes that give our skin its color. It is the most serious form of skin cancer because it can spread to any part of the body and could become fatal. The spread of cancer is referred to as metastasis.
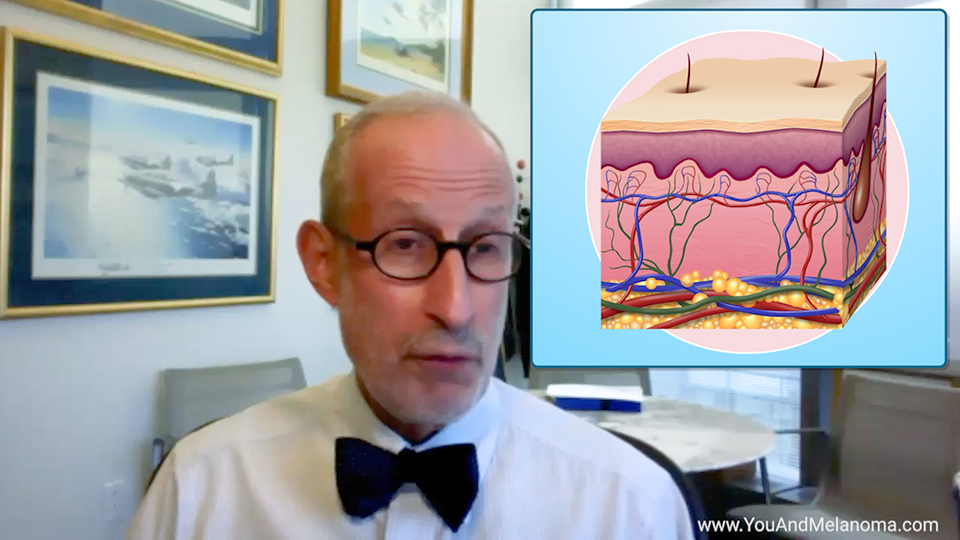
What is the function of the skin?
The skin is the body’s largest organ, with a total area of about 20 square feet. The skin performs many functions: It is a barrier that protects us from germs and the weather. It helps regulate body temperature. It allows us to sense heat, cold, touch, and pain.
What is the function of the skin?
Lymph nodes – small organs made up of clusters of different types of cells that belong to the immune system – are located throughout the body. Some are close to the skin, others are in deeper tissues. When melanoma starts to spread, it often travels first to a nearby lymph node and grows there.
What causes melanoma? – Malignancy
Cancer starts when cells become malignant – that is, they start to grow and divide uncontrollably, forming a tumor, and gain the ability to spread to other parts of the body. Melanoma is caused by melanocytes that have become malignant.
What causes melanoma? – Ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet, or UV, rays, are a major cause of melanoma. Most UV comes from sunlight. UV rays can also come from other sources, such as tanning beds.
UV damages the genetic material, or DNA, in melanocytes and skin cells. This causes changes in the genes that control how the cells grow and divide. Over time, these cells may become malignant. The damage to DNA may occur many years before cancer develops.
What causes melanoma? – Family history
Some gene changes that increase risk for melanoma run in families. These gene changes are called mutations. Around one out of every 10 people who get melanoma have at least one close relative – such as a parent, child, or sibling – who also had melanoma. A parent with a mutation has a 50-50 chance of passing it on to a child.
What are the signs of melanoma?
The most important sign of melanoma is a new spot, or mole, on the skin; a spot that is changing in size, shape, or color; a spot that bleeds; or an “ugly duckling” that looks different from other spots. Doctors call spots like these lesions. A lesion is an area of abnormal or damaged tissue.
Other signs to look for are a sore on the skin that doesn’t heal or a mole that’s red, swollen, itchy, tender, bleeding, or painful.
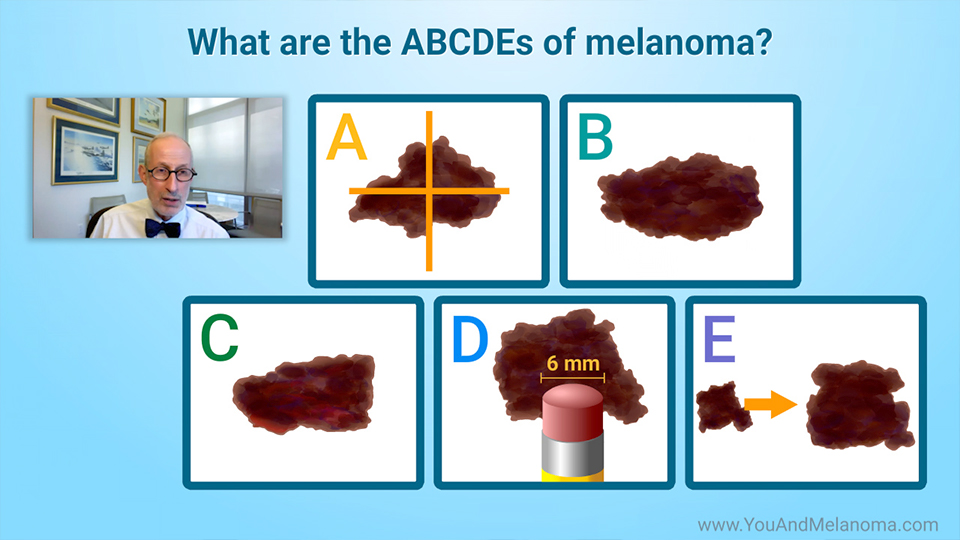
What are the ABCDEs of melanoma? – A
Look for these signs when checking moles on your skin:
A – An asymmetrical, or irregular, shape
What are the ABCDEs of melanoma? – B
B – An irregular or uneven border
What are the ABCDEs of melanoma? – C
C – More than one color in the same lesion
What are the ABCDEs of melanoma? – D
D – A diameter bigger than a pencil eraser (about 6 millimeters)
What are the ABCDEs of melanoma? – E
E – evolution, or change, in the size or color of a mole.
What should I do if I find an ABCDE sign?
If you notice any of these signs, make an appointment right away to have a dermatologist or primary care physician examine your skin.
What is melanoma staging? – Stage 0
Staging is a system for describing the size of the main tumor, whether it has spread, and if so, how far.
Stage 0 melanoma is confined to the top layer of the skin. Doctors call it melanoma in situ, which means “in its original place.”
What is melanoma staging? – Stage I or II
Stage I or II or “local” melanoma is deeper than Stage 0 but still confined to the skin. It starts between the outer skin (epidermis) and inner skin (dermis) and can spread into the inner skin.
What is melanoma staging? – Stage III
In Stage III or “loco-regional” melanoma, cancer cells have spread to nearby skin or to lymph nodes.
What is melanoma staging? – Stage IV
In Stage IV or “advanced” melanoma, cancer cells have spread to distant parts of the body.
Can melanoma be prevented? – Safe sun practices
Research suggests that nine out of 10 melanomas are caused by too much UV exposure.
You can prevent melanoma by using safe sun practices when you are outdoors.
Seek shade. Try to confine outdoor activities to before 10 AM and after 4 PM. The sun’s rays are strongest between 10 AM and 4 PM.
Can melanoma be prevented? – Avoid sunburn
Avoid getting sunburned. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a sun protection factor, or SPF, of at least 30 every day – even in winter, or when it’s cloudy. And, don’t forget to re-apply sunscreen if you are swimming or sweating.
Can melanoma be prevented? – Protective clothing
Wear protective clothing if you will be out in the sun for a prolonged period of time. This can include: a long-sleeved shirt, long pants, a wide-brimmed hat, and sunglasses.
Can melanoma be prevented? – Avoid tanning
Avoid tanning – whether intentionally or unintentionally. And stay away from sun lamps and tanning beds.
Can melanoma be prevented? – Monthly skin exam
And finally, you can be proactive in preventing melanoma by examining your skin carefully once a month.
What to do if you see something that concerns you
If you see anything that concerns you, make an appointment right away to have your primary care practitioner or dermatologist examine your skin.
This slide show describes the causes of melanoma and the signs to watch for (called the ABCDEs of melanoma). It also provides an overview of how melanoma is staged, what you should do if you notice any signs, and the steps you can take to protect your skin and prevent melanoma.
-
Share with family and friends:
Click here to take our SURVEY
Your feedback is important to us! We will use your feedback to develop future areas of content about melanoma which will help other patients, caregivers, and families.