Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) Cell Therapy in Melanoma
This slide show is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor about any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Your immune system naturally produces T-cells
When cancer cells first appear in your body, your immune system naturally produces a specific type of immune cell, called a T-cell, that can recognize and attack tumors.
This is part of your natural immune response.
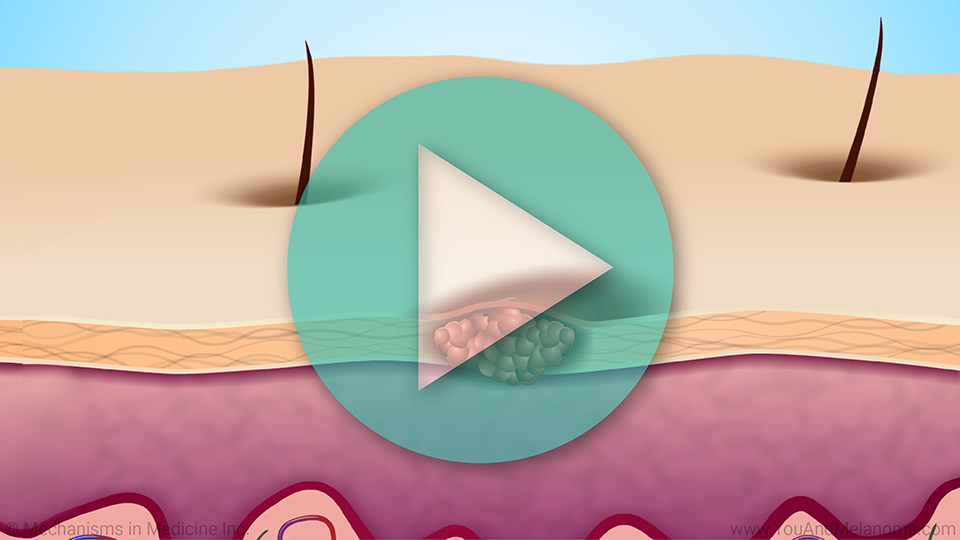
T-cells infiltrate the tumor to fight cancer
When T-cells go inside, or infiltrate, your tumor, they are called tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, or TIL.
TIL can naturally fight cancer cells.
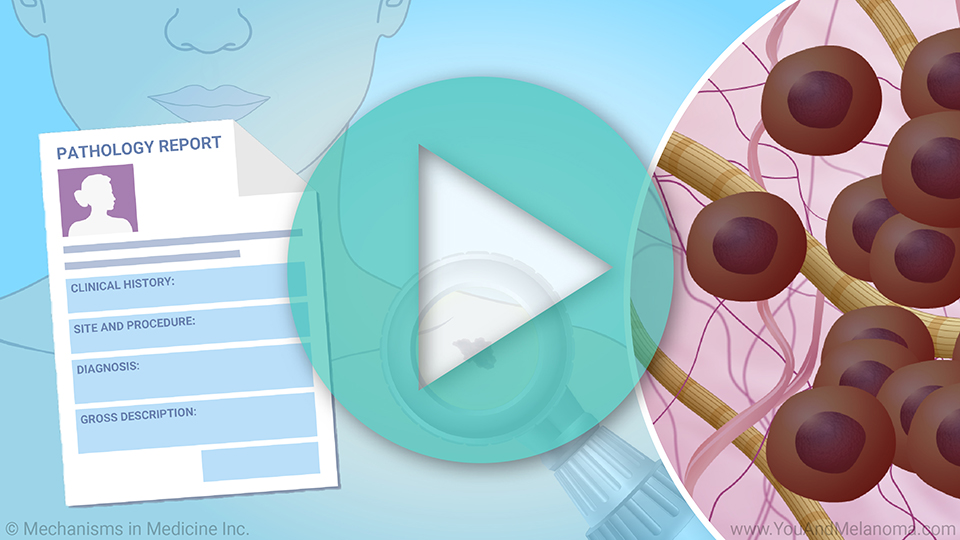
Cancer evades the natural immune response
Unfortunately, in some cases, cancer cells find ways to evade TIL and overpower your body's immune defenses. When this happens, your natural TIL may become ineffective or there may be too few of them to fight the cancer.
What is TIL Cell Therapy?
TIL Cell Therapy, or Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocyte Cell Therapy, is a new type of immunotherapy that utilizes TIL to attack cancer cells.
TIL Cell Therapy is now an FDA-approved treatment for non-uveal melanoma. In addition, researchers are conducting many clinical trials of potential new TIL treatments.
How does TIL Cell Therapy work?
TIL Cell Therapy is an individualized therapy that fights cancer by adding billions of your own TIL to your body.
How does TIL Cell Therapy work?
TIL are removed from your body by taking out a tumor, then multiplying the TIL in a manufacturing facility.
When the manufactured TIL are administered, they can kill cancer cells just like your natural TIL, but billions of cells can be more effective than the smaller number that were originally in the tumor.
How does TIL Cell Therapy work?
In TIL Cell Therapy, TIL circulate in your bloodstream and travel into a tumor, where they recognize specific substances called tumor-associated antigens.
How does TIL Cell Therapy work?
TIL Cell Therapy delivers TIL that are toxic to the cancer cells and destroy the tumor.
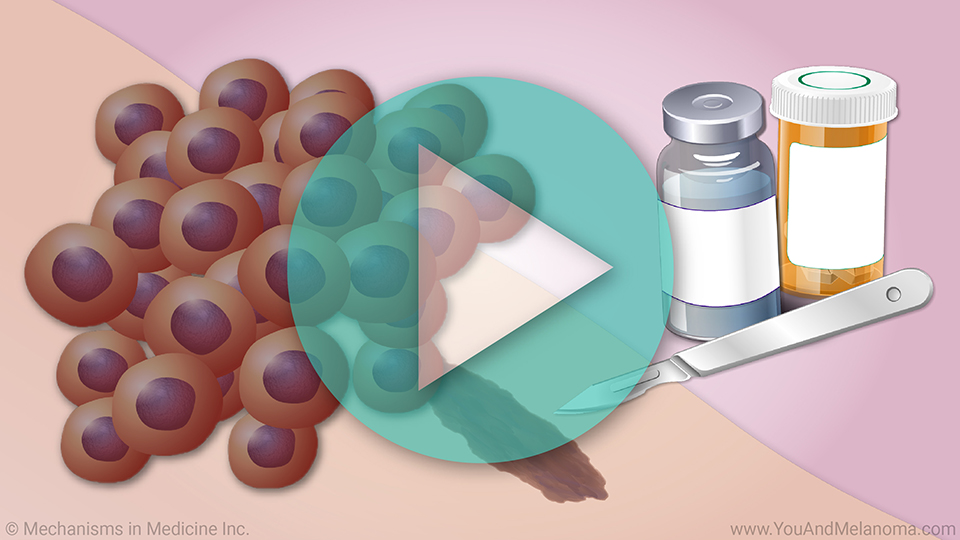
Preparing TIL Cell Therapy in the manufacturing facility
If TIL Cell Therapy is an option for you, doctors will surgically remove a small piece of your melanoma tumor and send it to the manufacturing facility.
Preparing TIL Cell Therapy in the manufacturing facility
The TIL are removed from your tumor and grown in a lab with substances that help them survive and multiply. Over several weeks, the TIL multiply into the billions.
Preparing TIL Cell Therapy in the manufacturing facility
When the manufacturing process is finished, the TIL product is frozen and shipped to the treating center in preparation for IV administration.
Step 1: Receiving chemotherapy before TIL Cell Therapy infusion
When manufacturing is complete, it is time to receive the TIL infusion. You will come to the hospital for 5 to 7 days beforehand for chemotherapy to reduce the number of your body’s existing immune cells. This prepares the body to receive the TIL and is a necessary part of the TIL treatment. You may stay in the hospital during chemo or go home at the end of each day.
Step 2: Receiving TIL Cell Therapy infusion
Next, you will receive the infusion of TIL Cell Therapy grown in the manufacturing facility personally for you.
You will be hospitalized during this entire process so your doctor can watch for any negative side effects.
Circulating TIL can attack tumor cells
Once infused back into you, TIL can effectively recognize and attack the tumor cells.
TIL can increase more than 1000 times after IV infusion
The new TIL continue increasing once they are in your body. They can increase more than 1000 times after IV infusion, and they continue to replicate in your body over time.
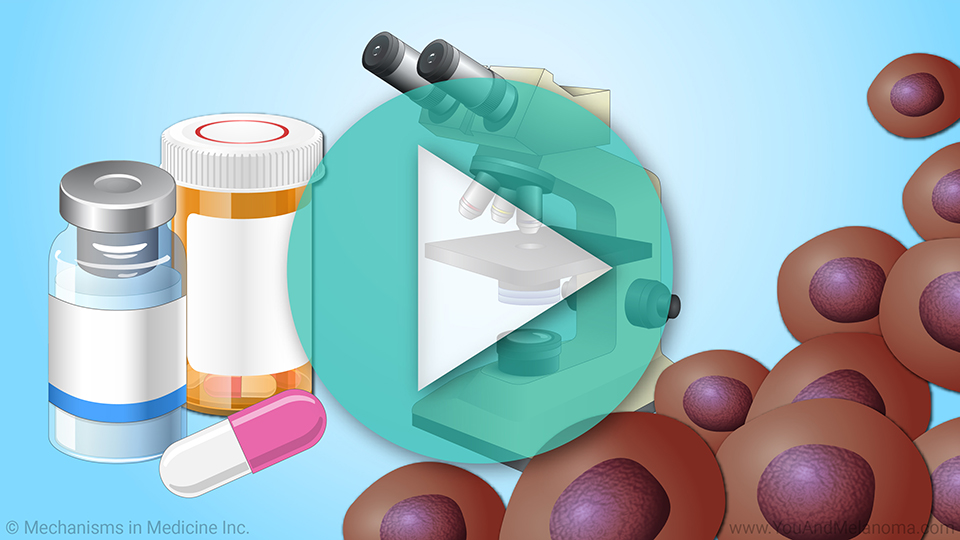
Step 3: Receiving IL-2 following TIL Cell Therapy infusion
Following your TIL Cell Therapy infusion, you will receive up to 6 doses of IL-2 to promote activation, proliferation, and tumor-killing activity of the TIL.
The only patients who might not receive IL-2 are those taking part in a clinical trial. For regular TIL treatment, however, you must be able to receive IL-2.
Side effects of TIL Cell Therapy
TIL Cell Therapy can cause side effects. The most common include chills, fever, low white blood cell count, fatigue, low red blood cell count, fast or irregular heartbeat, rash, low blood pressure, and diarrhea.
How to know if TIL Cell Therapy is right for you
You and your doctor will decide if TIL Cell Therapy is right for you.
You must be healthy enough for chemotherapy before the TIL infusion, infusion itself, and the IL-2 treatment. Your cancer must also be stable enough for you to wait several weeks while TIL are prepared in the manufacturing facility.
When is TIL Cell Therapy used?
TIL Cell Therapy is approved for people whose tumors have spread or cannot be surgically removed and who may have already had certain other melanoma treatments. Your doctor will talk with you about whether TIL Cell Therapy is an option for you.
When is TIL Cell Therapy used?
The FDA-approved therapy, called lifileucel, continues to be studied in clinical trials for melanoma and is also being studied for its effectiveness against other cancers.
Is TIL Cell Therapy given more than once?
TIL Cell Therapy is a one-time treatment. You do not need repeated treatments, or maintenance therapy.
How effective is TIL Cell Therapy for melanoma?
In the study that led to FDA approval, cancer disappeared or was reduced in approximately 30% of patients.
How effective is TIL Cell Therapy for melanoma?
Some patients had a complete response, which means cancer is no longer seen on body scans. A small number of people treated with TIL Cell Therapy have been cancer-free for years, including some for over 10 years.
People treated with TIL Cell Therapy lived twice as long as those treated with IL-2
TIL Cell Therapy has helped people with melanoma live longer than people treated with IL-2 alone. In one recent study, people receiving TIL Cell Therapy lived more than twice as long as those who did not.
A promising treatment for melanoma and other cancers
Because TIL Cell Therapy is such a promising treatment for melanoma and other cancers, many clinical trials are going on now. Visit cancer.gov and search for "TIL Cell Therapy" or "lifileucel" to find them.
References
- Badalamenti G, Fanale D, Incorvaia L, Barraco N, Listì A, Maragliano R, Vincenzi B, Calò V, Iovanna JL, Bazan V, Russo A. Role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with solid tumors: Can a drop dig a stone? Cell Immunol. 2019 Sep;343:103753.
- Monjazeb AM, Zamora AE, Grossenbacher SK, Mirsoian A, Sckisel GD, Murphy WJ. Immunoediting and antigen loss: overcoming the achilles heel of immunotherapy with antigen non-specific therapies. Front Oncol. 2013 Jul 26;3:197.
- Rosenberg SA, Restifo NP. Adoptive cell transfer as personalized immunotherapy for human cancer. Science. 2015 Apr 3;348(6230):62-68.
- Betof Warner A, Hamid O, Komanduri K, Amaria R, Butler MO, Haanen J, Nikiforow S, Puzanov I, Sarnaik A, Bishop MR, Schoenfeld AJ. Expert consensus guidelines on management and best practices for tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte cell therapy. J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Feb 29;12(2):e008735.
- Chesney J, Lewis KD, Kluger H, Hamid O, Whitman E, Thomas S, Wermke M, Cusnir M, Domingo-Musibay E, Phan GQ, Kirkwood JM, Hassel JC, Orloff M, Larkin J, Weber J, Furness AJS, Khushalani NI, Medina T, Egger ME, Graf Finckenstein F, Jagasia M, Hari P, Sulur G, Shi W, Wu X, Sarnaik A. Efficacy and safety of lifileucel, a one-time autologous tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) cell therapy, in patients with advanced melanoma after progression on immune checkpoint inhibitors and targeted therapies: pooled analysis of consecutive cohorts of the C-144-01 study. J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Dec;10(12):e005755.
- Amtagvi (lifileucel). Last revised: December 2024.
https://www.amtagvi.com
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to lifileucel for unresectable or metastatic melanoma. Last revised: February 16, 2024.
https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-lifileucel-unresectable-or-metastatic-melanoma
- Rohaan MW, Borch TH, van den Berg JH, Met Ö, Kessels R, Geukes Foppen MH, Stoltenborg Granhøj J, Nuijen B, Nijenhuis C, Jedema I, van Zon M, Scheij S, Beijnen JH, Hansen M, Voermans C, Noringriis IM, Monberg TJ, Holmstroem RB, Wever LDV, van Dijk M, Grijpink-Ongering LG, Valkenet LHM, Torres Acosta A, Karger M, Borgers JSW, Ten Ham RMT, Retèl VP, van Harten WH, Lalezari F, van Tinteren H, van der Veldt AAM, Hospers GAP, Stevense-den Boer MAM, Suijkerbuijk KPM, Aarts MJB, Piersma D, van den Eertwegh AJM, de Groot JB, Vreugdenhil G, Kapiteijn E, Boers-Sonderen MJ, Fiets WE, van den Berkmortel FWPJ, Ellebaek E, Hölmich LR, van Akkooi ACJ, van Houdt WJ, Wouters MWJM, van Thienen JV, Blank CU, Meerveld-Eggink A, Klobuch S, Wilgenhof S, Schumacher TN, Donia M, Svane IM, Haanen JBAG. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte therapy or ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2022 Dec 8;387(23):2113-2125.